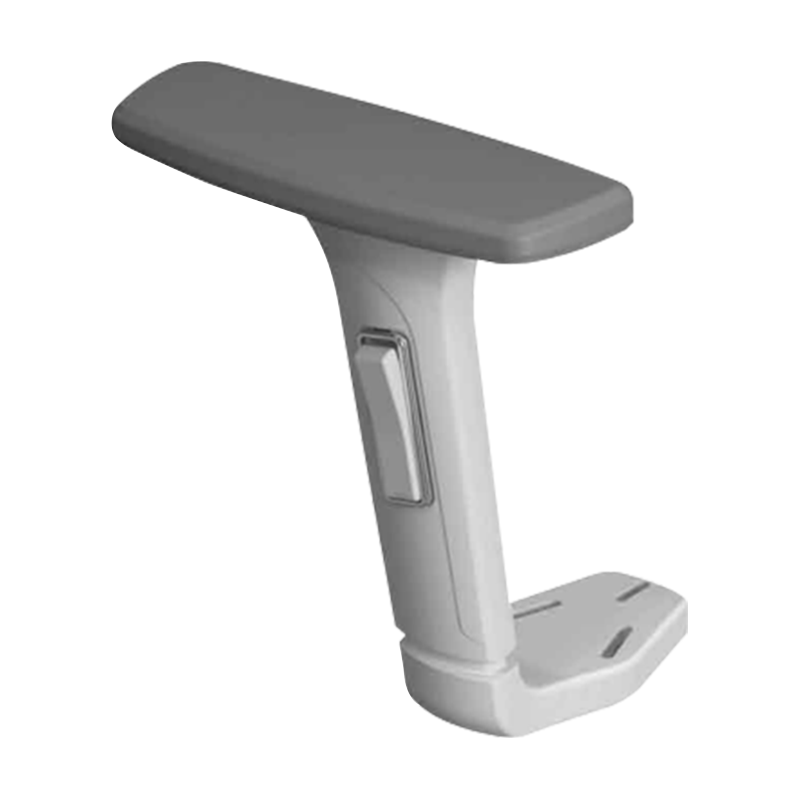
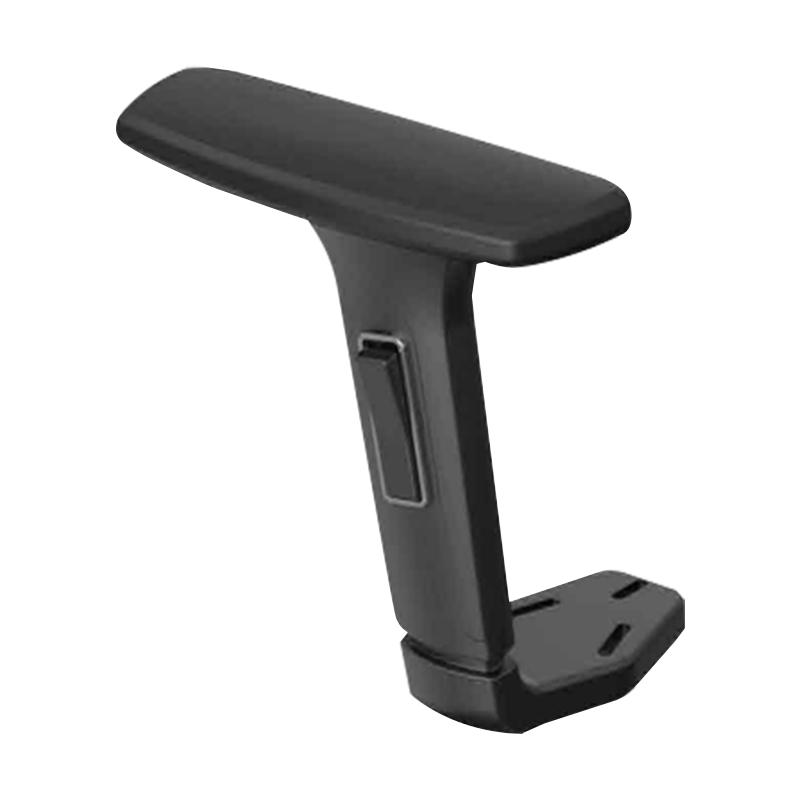
Product category
Contact Us
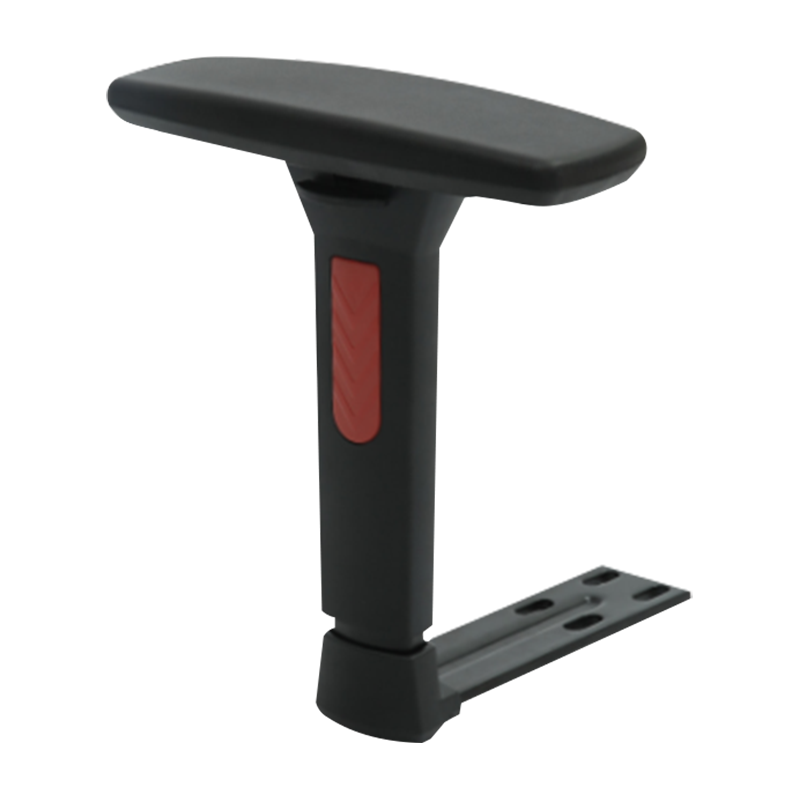
Ergonomic 1D Adjustable Office Chairs Armrest Suppliers
-
XL-303-1D
303 Gaming Chair Armrest 1D 3 Holes, Up and Down Adjustable Armrest Replacement
-
XL-302-1D
302 Adjustable Nylon 1D Armrest for Mesh Office Computer Chair
-
XL-301-1D
301 Adjustable 1D Armrest for Mesh Office Computer Chair
-
XL-703-1D
703 Ergonomic Office Chair 1D Armrest
-
XL-701-1D
701 Liftable and Adjustable Nylon 1D Armrest
-
XL-flat tube handrail
Flat Tube Armrest, Adjustable Office Chair Gaming Chair Armrest 1D
-
XL-5508A-1D
5508A-1D Chrome Adjustable Ergonomic Armrest
-
XL-5508-1D
5508-1D Ergonomic Office Chair Adjustable Armrest Assembly Chrome Plated
-
XL-705A-1D
705A-1D Chrome-Plated Adjustable Armrest Parts
-
XL-705-1D
705-1D Ergonomic Multifunctional Office Chair Armrest Accessories

About Us
Our company is also constantly innovating and expanding, pursuing higher quality products. We welcome sincere cooperation with colleagues in the furniture field to create a win-win situation together.
News
Industry Knowledge Extension
How to achieve multi-dimensional adjustment (height, angle, front and back) of ergonomic adjustable office chair armrests?
Height adjustment: technical logic from "adapting to height" to "dynamic support"
The height adjustment of office chair armrests is the most basic ergonomic design. Its core goal is to allow the elbows to easily rest on the armrests when the arms are naturally drooping, avoiding muscle tension caused by the shoulders hanging in the air. From the perspective of technical implementation, height adjustment is mainly achieved through the following structures and mechanisms:
1. Mechanical locking height adjustment: a reliable choice for basic models
Core structure: mostly using a combination of "gas rod + slot" or "gear rack". Taking the 1D armrest as an example, its up and down adjustment function is usually achieved through a built-in gas pressure lifting rod - the nitrogen in the gas pressure rod is pressurized to support the weight of the armrest. When the user presses the release button, the piston inside the gas pressure rod loosens, and the armrest can be raised and lowered freely. After releasing the button, the slot will be locked at the preset height.
Technical details: The gear rack structure drives the rack up and down by rotating the handle. The gear teeth mesh with the rack to form a mechanical lock with an accuracy of 1-2cm, which is suitable for scenes with low requirements for height adjustment accuracy, such as entry-level office chairs.
2. Electric drive height adjustment: intelligent and accurate upgrade
Driving principle: High-end ergonomic chairs will be equipped with a motor drive system, which controls the forward and reverse rotation of the micro motor through buttons to drive the screw nut mechanism to rise and fall. For example, the height adjustment of the armrests of some models can achieve 0.5cm-level precision control, suitable for users with a height of 150-190cm.
Technical extension: The company may combine advanced production technologies in research and development, such as CNC-processed gas rod accessories to ensure the smoothness and locking reliability of the lifting process. The optimization of the production process by its professional team (such as strict quality inspection links) can reduce problems such as gas rod leakage and jamming.
3. Ergonomic design points
The height adjustment range usually needs to cover 15-25cm to meet the needs of users of different heights. For example, the elbow height of a user with a height of 160cm is about 65-70cm, while that of a user with a height of 180cm is 75-80cm. The adjustable armrest needs to be able to flexibly adapt to this range.
In product design, international quality standards may be followed to test the load-bearing capacity of the armrest (such as static load-bearing capacity of more than 50kg) to ensure that the height adjustment mechanism is not easily deformed during long-term use.
Angle adjustment: functional evolution from "fixed support" to "dynamic fit"
The angle adjustment of the armrest (such as internal rotation, external rotation or forward tilt, backward tilt) mainly solves the posture requirements of the arm in different office scenarios, such as elbow extension when typing, arm extension when writing, etc. Its technical implementation can be divided into the following types:
1. Hinge angle adjustment: basic rotation structure
Structural design: The armrest and the bracket are connected through the hinge shaft, and the outer periphery of the hinge shaft is wrapped with a damping sleeve or spring. When the user manually bends the armrest, the damping sleeve provides resistance to maintain the angle, and the spring can assist in resetting. The common angle adjustment range is ±15°-±30°.
Application case: In the diversified product line, some mid-range models may adopt this structure. Its design team ensures the smoothness of angle adjustment and locking stability by optimizing the material of the hinge shaft (such as high-strength aluminum alloy) and the friction coefficient of the damping sleeve.
2. Multi-link angle adjustment: precise control of complex postures
Mechanical principle: Through the linkage of multiple sets of linkage mechanisms, the multi-angle compound adjustment of the armrest can be realized. For example, the forward tilt angle adjustment can be achieved by pushing the front end of the armrest down through the linkage, and the rear end of the armrest is lifted up by stretching the linkage when tilting backward, and the internal rotation/external rotation is achieved by rotating the linkage in the horizontal direction.
Technical advantages: This structure can achieve "multi-angle linkage adjustment", such as the armrest automatically tilts forward 10° and rotates outward 5° when the user is typing, which fits the natural posture of the arm and reduces wrist pressure. If Anji Xielong Furniture Co., Ltd. develops such products, it may rely on its advanced production equipment (such as stamping dies and CNC machining centers) to ensure the accuracy of the linkage and avoid looseness and abnormal noise.
3. Adaptive angle adjustment: intelligent sensing and dynamic response
Frontier technology: Some high-end models are equipped with pressure sensors. When the arm is placed on the armrest, the sensor detects the pressure distribution and drives the motor to adjust the angle of the armrest. For example, when the weight of the arm is concentrated on the front end of the armrest, the system automatically tilts forward 5° to disperse the pressure.
Ergonomic logic: The core of angle adjustment is "matching the trajectory of elbow joint movement". Studies have shown that when the elbow moves naturally, the internal rotation/external rotation angle is about 20°, and the forward/backward tilt is about 15°. Reasonable angle adjustment can reduce shoulder muscle tension by more than 30%.
Front-to-back adjustment: spatial expansion from "fixed position" to "scene adaptation"
The front-to-back adjustment function enables the armrest to move with the user's sitting posture. For example, the armrest extends forward when leaning forward to work, and moves backward when leaning back to rest. Its technical implementation relies on the following mechanisms:
1. Slide rail front-to-back adjustment: the basic solution for linear movement
Structural composition: It consists of a slide rail fixed to the chair body and a slider installed on the armrest. The slider has built-in balls or rollers to reduce friction. The user unlocks the slider by pulling the handle or button, and pushes the armrest forward and backward. The adjustment range is usually 5-10cm.
Locking method: common magnetic or slot locking. The magnetic type uses a strong magnet to absorb the slider, which is suitable for light adjustment; the slot type uses a gear to mesh with the slide rail rack, and has a stronger load-bearing capacity. Anji Xielong Furniture Co., Ltd. may use the latter in the design to ensure the reliability of locking under heavy weight.
2. Linkage-type front and rear adjustment: intelligent design synchronized with the seat
Linkage logic: The front and rear adjustment of the armrests of some high-end ergonomic chairs is linked with the seat back. For example, when the user lies back, the backrest angle increases, and the linkage mechanism pushes the armrests backward synchronously to keep the relative position of the arms and the body unchanged.
Technical difficulties: The linkage ratio needs to be accurately calculated. For example, when the backrest is tilted back 10°, the armrest moves back 2cm. This requires the design team to have rich experience in mechanical analysis. The professional team may optimize the linkage parameters through CAD simulation and repeated testing.
3. Ergonomic application scenarios
Forward office: The armrest extends 5cm forward to support the wrist and reduce the arm hanging in the air when typing on the keyboard;
Back rest: The armrest moves back and is appropriately raised, which can be used as an elbow support, and cooperates with the headrest to form a relaxed posture;
Customization needs: The customization service provided by Anji Xielong Furniture Co., Ltd. can adjust the front and rear adjustment range according to the user's body shape (such as arm length), for example, the adjustment range is extended to 12cm for long-arm users.
Integrated design and quality control of multi-dimensional adjustment
1. Integrated structural design
The height, angle, and front and rear adjustment functions are often combined through an "integrated bracket", such as the bottom of the bracket is connected to the pneumatic rod (height adjustment), the middle is connected to the armrest through a hinge (angle adjustment), and the top slide rail realizes forward and backward movement. This design needs to balance the smoothness of adjustment in each dimension to avoid structural interference. Modular assembly may be used in production, and precision molds are used to ensure that the tolerance of each component is controlled within 0.5mm.
2. Support of materials and processes
Material of key components: The core components of the adjustment mechanism (such as pneumatic rods and hinge shafts) are mostly made of high-strength steel or aviation aluminum alloy, and the surface is anodized for wear and corrosion resistance;
Quality standards: The company strictly follows the international quality system and performs fatigue tests on each batch of armrest accessories (such as 5000 cycles for height adjustment and 3000 cycles for angle adjustment) to ensure stable performance in long-term use.
3. Comprehensive optimization of ergonomics
The ultimate goal of multi-dimensional adjustment is to achieve "dynamic fit", for example:
For a user with a height of 170cm, when the armrest height is adjusted to 70cm, the shoulder muscle pressure is minimal when the armrest is tilted forward 5° and extended 3cm;
In the development of new products, such ergonomic parameters may be incorporated into product design through user surveys and data collection, such as upgrading the 1D armrest to a 3D adjustment function to meet more complex usage needs.



 English
English  Español
Español  عربى
عربى