Web Menu
Product Search
Home / News / Industry News / Assessing the Adjustment Range of the Office Chair 3D Armrest for Universal User Support
Industry News
All the news you need to know about T-LORD
Assessing the Adjustment Range of the Office Chair 3D Armrest for Universal User Support
2025-12-24
- 1 The Criticality of Armrest Adjustability
- 2 Defining 3D Adjustability: Axes of Movement
- 3 Matching Adjustability to User and Desk Dimensions
- 4 The 3D vs. 4D Technical Comparison
- 5 Manufacturing Quality and Reliability
- 6 Conclusion: Specifying Versatile Ergonomic Accessories
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The Criticality of Armrest Adjustability
Translating Flexibility into User Well-being
- In the competitive office furniture sector, the
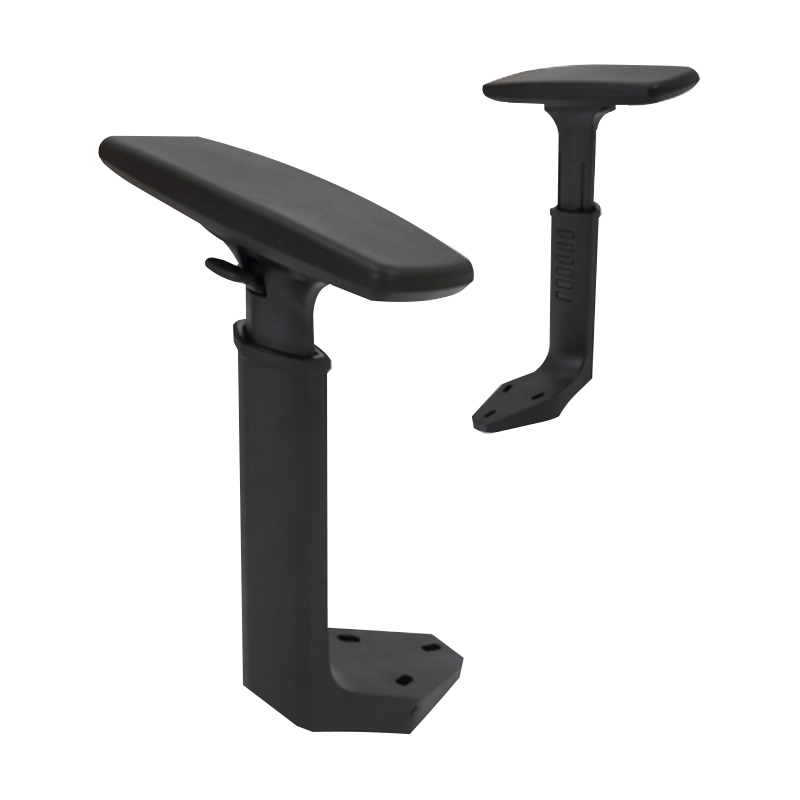
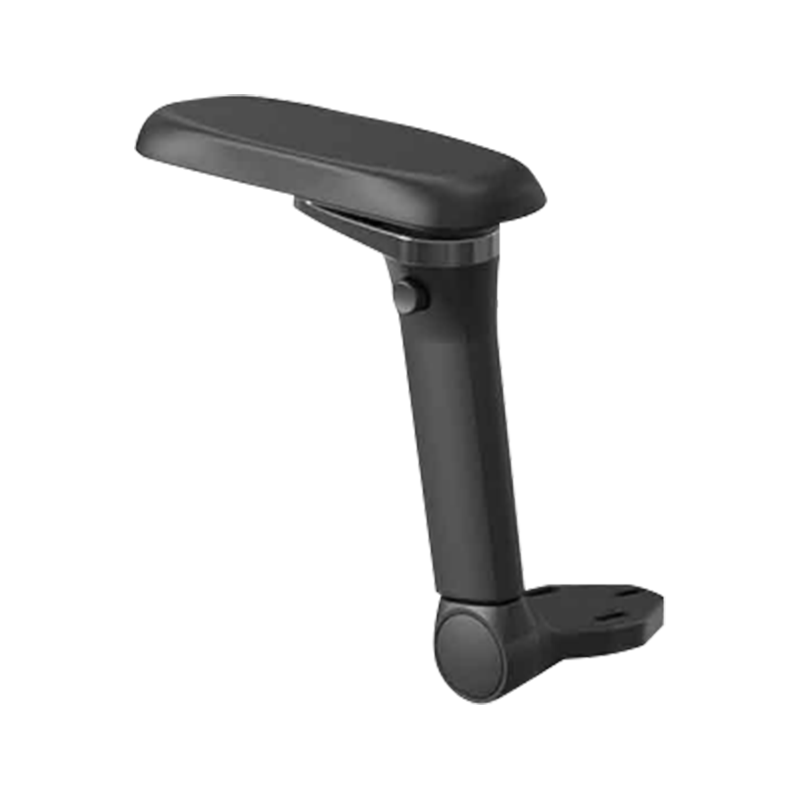
Office Chair 3D Armrest is a primary selling point, directly influencing user comfort and long-term musculoskeletal health. Its core function is to allow the user to support their forearms in a neutral posture—shoulders relaxed, elbows bent between 90 and 110 degrees—to minimize strain on the neck and upper back. - For B2B wholesalers and furniture manufacturers, ensuring the armrest mechanism offers a sufficient adjustment range is essential to successfully target a broad demographic, from the 5th percentile female to the 95th percentile male. Quality, precision, and adherence to ergonomic standards are the mission of manufacturers like Anji Xielong Furniture Co., Ltd., which specializes in R&D and production of adjustable armrests.
Defining 3D Adjustability: Axes of Movement
Vertical and Horizontal Range Specification
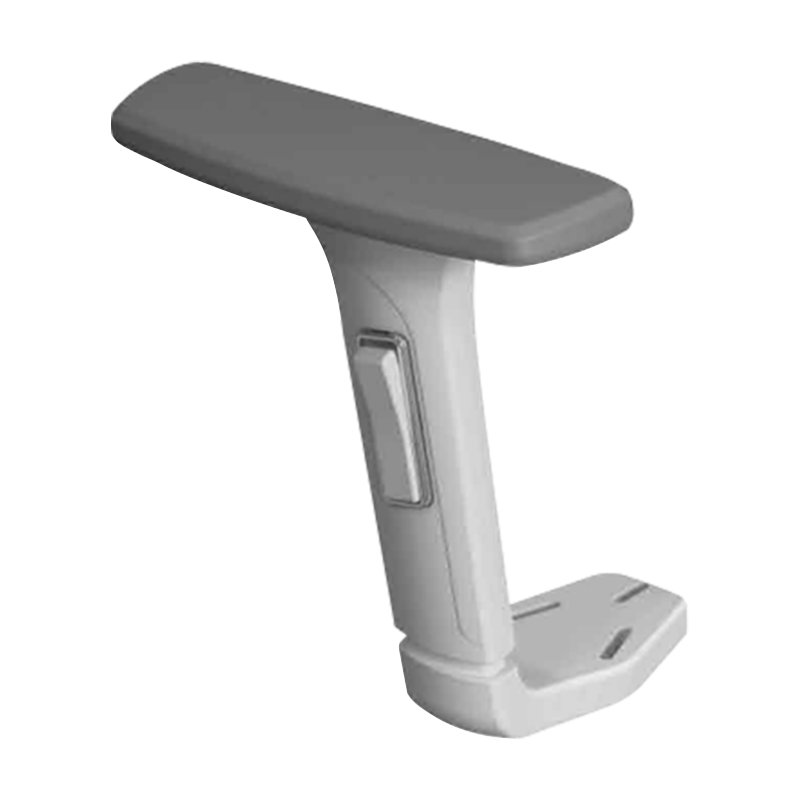
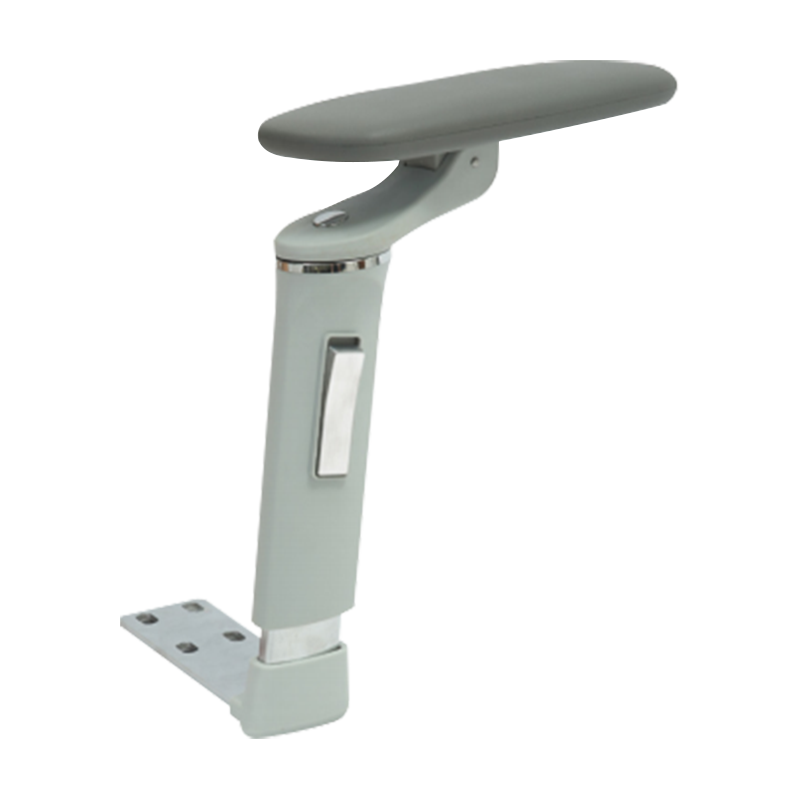
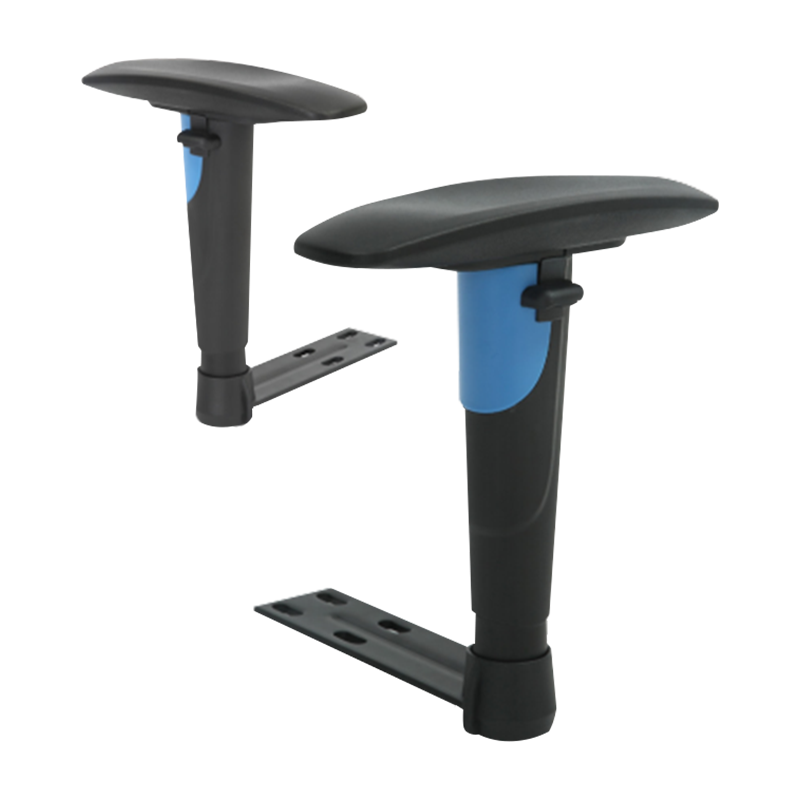
- The "3D" designation refers to three distinct, lockable axes of motion: Vertical Height, Depth (front-to-back), and Angle/Pivot (inward/outward swivel). The
3D adjustable armrest height range specification is arguably the most critical parameter, as it dictates the armrest's ability to align with the user's elbow height relative to the seat pan. - A typical professional-grade armrest should offer at least 100mm (approximately 4 inches) of vertical adjustment from the seat pan to accommodate variance in user height and seating style, preventing the shoulders from shrugging or drooping.
Depth and Width: Supporting Diverse Body Types
- Depth (front-to-back) adjustment is vital for ensuring the forearm pad supports the user regardless of their recline angle or proximity to the desk edge.
- The swivel or
Office chair armrest lateral adjustment mechanism allows users to adjust the width between the armrests. This is a crucial ergonomic feature, accommodating users with broad shoulders (requiring wider support) or allowing the armrests to be positioned closer for specific tasks like typing, promoting the ideal neutral elbow position.
Matching Adjustability to User and Desk Dimensions
Height Compatibility for Tall and Short Users
- Achieving
Ergonomic armrest adjustability for tall users demands mechanisms that extend high enough to meet a taller user's elbow when the chair is fully lowered. Conversely, for short users, the armrest must drop low enough to clear the underside of the desk and maintain a non-shrugged posture. - The failure to accommodate both extremes compromises the chair's universal appeal. The design must ensure the mechanism's structural integrity (lateral stability) is maintained across the entire vertical adjustment span.
Minimum Required Vertical Adjustment Range
The total required vertical travel is determined by the need to fit both extreme user sizes while achieving the optimal elbow angle.
| User Percentile | Armrest Height Required (Above Seat Pan, Typical) | Critical Design Consideration |
| 5th Percentile Female (Short) | 18 - 22 cm | Minimum height must allow desk clearance. |
| 95th Percentile Male (Tall) | 28 - 32 cm | Maximum height must maintain vertical stability. |
Desk Height Synchronization and Clearance
- The utility of any armrest is limited by its compatibility with the workspace. The
Optimal desk height armrest compatibility guide dictates that the armrest, at its lowest functional point, must be capable of fitting beneath the desk (typically $70$ cm or $27.5$ inches minimum clearance) to allow the user to pull the chair close to the workstation. - Any obstruction forces the user to sit too far back, compromising lumbar support and increasing reach distance, thus defeating the primary ergonomic goal.
The 3D vs. 4D Technical Comparison
Selecting the Appropriate Mechanism Complexity
- The core difference between the
Office Chair 3D Armrest and its 4D counterpart lies in the fourth axis, which is typically horizontal lateral movement (sliding the entire pad directly inward/outward without pivoting). - For most standard office tasks, a well-engineered 3D mechanism provides the essential height, depth, and pivot required for optimal ergonomic posture. The added complexity of 4D, while offering fine-tuning, must be balanced against potential failure points and manufacturing cost.
Comparison of 3D vs 4D Office Chair Armrests
Selection is based on the priority given to cost versus absolute customization.
| Adjustment Feature | 4D Armrest (Typical) | Functional Benefit | |
| Vertical Height | Yes | Yes | Elbow-to-Desk Alignment |
| Lateral Width/Pivot | Pivot/Swivel Only | Pivot and Direct Lateral Slide | Shoulder Width Accommodation |
| Complexity & Cost | Moderate | High | Customization vs. Value |
Manufacturing Quality and Reliability
The Foundation of Durable Adjustability
- The true measure of an
Office Chair 3D Armrest lies in the durability of its locking mechanisms. A failure to lock securely under repeated load (e.g., a user leaning on the armrest to stand up) will render the ergonomic benefit useless. - Anji Xielong Furniture Co., Ltd., which integrates R&D and production, adheres to the principle of "Quality first, customers first." This means utilizing robust injection-molded components, high-strength internal metal sliders, and precision-engineered locking teeth to ensure that the specified
3D adjustable armrest height range specification remains locked throughout the chair's service life, providing reliable and high-quality accessories to our partners.
Conclusion: Specifying Versatile Ergonomic Accessories
- A well-designed
Office Chair 3D Armrest with sufficient vertical travel and a robustOffice chair armrest lateral adjustment mechanism offers the required versatility to support the majority of users and desk setups. B2B buyers must prioritize mechanisms that meet the full required adjustment range, ensuring their products achieveErgonomic armrest adjustability for tall users and short users, thereby maximizing the product's marketability and ergonomic compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: What is the minimum vertical height range considered acceptable for a professional-grade
Office Chair 3D Armrest ?
A: A minimum vertical adjustment range of $100$mm (approximately 4 inches) is generally considered the technical baseline for accommodating the majority of the user population while ensuringOptimal desk height armrest compatibility guide . - Q: What is "armrest creep" and how can it be avoided?
A: Armrest creep is the gradual slippage of the armrest height mechanism under load. It is avoided by utilizing high-tolerance, positive mechanical locking mechanisms (e.g., teeth or robust hydraulic/friction locks) rather than relying solely on friction, which is a key quality control aspect for manufacturers. - Q: How does the
Office chair armrest lateral adjustment mechanism impact the overall footprint of the chair?
A: Mechanisms that allow the arm pads to pivot inward can temporarily reduce the required lateral space, while those designed forErgonomic armrest adjustability for tall users with broad shoulders must ensure the armrest does not extend too far beyond the seat base, potentially causing clearance issues in tight spaces. - Q: Besides height, why is the depth adjustment critical in a
3D adjustable armrest height range specification ?
A: Depth adjustment ensures the forearm support ends slightly before the elbow, preventing pressure on the elbow joint (a potential cause of ulnar nerve issues) and allowing the user to correctly position their forearms based on the task (e.g., pulling the pad back when typing, pushing forward when mousing). - Q: When comparing the
Comparison of 3D vs 4D office chair armrests , does 4D always equate to better ergonomics?
A: Not necessarily. While 4D offers greater micro-adjustments, its ergonomic advantage over a high-quality, well-engineered 3D armrest is marginal for most users. The quality and stability of the mechanism are often more important than the quantity of axes.
PREV:What Exactly is a 5D Armrest, and How Does It Differ from Standard Ergonomic Chairs?NEXT:Achieving 5D Armrest Mounting Plate Standardization and Design Harmony

 Feel free to contact us
Feel free to contact us
Anji Xielong Furniture Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer integrating R&D, production and sales of adjustable armrests for office chairs.
- Product Fast Links
- Office Chair Armrest
- Hardware Steel Plate
- Polyurethane PU Surface
- Casters
- Contact Information
- Tangpu Industrial Park, Anji County, Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
- [email protected]
- +86-13567973388



 English
English  Español
Español  عربى
عربى